Fractal Art Week
Today, we will chat about L-systems and what they have to do with fractals
Substitution systems
In a substitution system, we use a set of rules to transform elements of a sequence. Like this: Rule [1 → 0 and 0 → 11]
Starting sequence: 01
Step 1: 110
Step 2: 0011
Step 3: 111100
Step 4: 00001111
Step 5: 111111110000
...
Starting sequence: 01
Step 1: 110
Step 2: 0011
Step 3: 111100
Step 4: 00001111
Step 5: 111111110000
...
L-systems can not only be used to generate fractals, but also to model many processes (plant gowth, for example - l-systems are great for making procedural trees
Koch Curve
Lets take a look at a simple example: Koch Curve.The L-system notation for it is:
Rule: [F → F + F − F − F + F]
Start: F
Where F means "draw forward", + means "turn left 90°", and − means "turn right 90°".
Start: F

Step 1: F → F + F − F − F + F
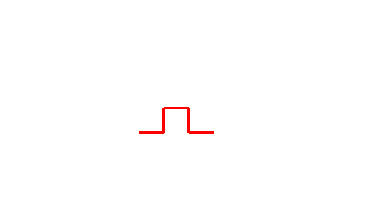
Step 2: F + F − F − F + F → F+F−F−F+F + F+F−F−F+F − F+F−F−F+F − F+F−F−F+F + F+F−F−F+F

You can see that, right now, it is actually not "substituting", but drawing forward. So the curve is not fitting a given shape, but expanding it at each step. In fractaling, though, its usually handier to actually replace elements.
For this, you would need to scale elements down - so the length of F+F−F−F+F is the same as the length of F from the previous step. With replacement, the steps above would look like:
Start

Step 1
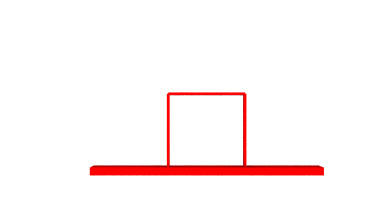
Step 2
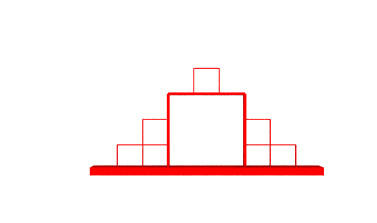
And 10 steps later...
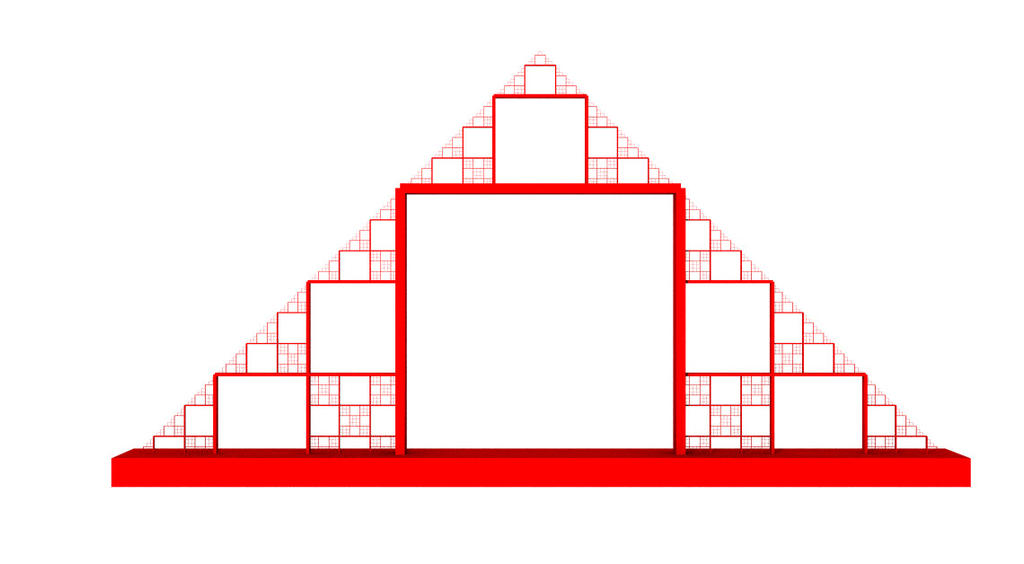
In Apophysis
This second "replacement" way can be easily implemented in Apophysis (and other IFS software).For example, the Koch Curve: our replacement rule is F → F + F − F − F + F. We will need 5 transforms, since we have 5 elemets replacing the original one on each step. As you can see on the picture above, the scale will be 1/3: the sequence F + F − F − F + F has a length 3F, and we need to scale it down so it is length F.
Now, time to position the transforms (all scaled down to 0.33333 of the original size).
- leave it at the origin
- Move to the right by 1/3 (length of the first F) and do the "+" - rotate by 90° CCW
- Move to the right by 1/3 (first transform) and move up by 1/3 (second transform). The rotation is a "+" then "−", which cancel themselves - so no rotation at all
- 1/3 right, 1/3 up, 1/3 right. For rotation, we have a "+ − −" which gives a "−": 90° CW
- 1/3 right, 1/3 up, 1/3 right and 1/3 down - so 2/3 right overall. Rotation: "+ − − +"
Basically, you draw 1 step of the L-System rule, with transforms. Compare the picture below (F → F + F − F − F + F step)

And the position of transforms:

Parameters: Koch Curve in Apo - in case you need them. Below, the look of the Koch Curve in Apo:

As an addition, you can "fill" the curve in: Koch Curve Filled.
